S4.
Let’s try to find the complementary function of the second ordered linear differential equation with constant coefficients at first.
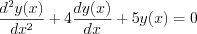
Let’s find the complementary function by the following formula 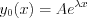
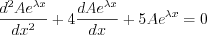
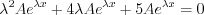
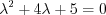 where the auxiliary equation is obtained. Roots of the second ordered polynomial equation:
where the auxiliary equation is obtained. Roots of the second ordered polynomial equation:
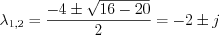
i.e.  and
and 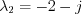 .
.
Consequently the solutions are 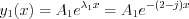 and
and 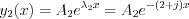
Linear combination of the two independent solution is also solution of the homogenous equation, meaning the complementary function will be the following:
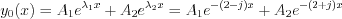
Let’s find the particular solution as 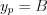 , where B is a constant value, due to the constant input function.
, where B is a constant value, due to the constant input function.
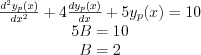
General solution of the inhomogeneous differential equation is:
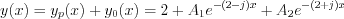
Let’s use the initial conditions, in order to determine 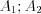 coefficients.
coefficients.
![$
\left.\begin{matrix}
y(0)=0\\
\\
\frac{dy(x)}{dx}\big{|}_{x=0}=0
\end{matrix}\right\}\rightarrow\begin{matrix}
2+A_{1}+A_{2}=0 \\
\\
\frac{dy(x)}{dx}\big{|}_{x=0}=\frac{d}{dx}\left[2+A_{1}e^{-(2-j)x}+A_{2}e^{-(2+j)x}\right]\big{|}_{x=0}=-(2-j)A_{1}-(2+j)A_{2}=0
\end{matrix}](lib/equation/pictures/48064076bac3a73a5495f42afe7fdeed.png)
Now the following set of two linear equations has to solve:
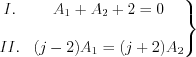
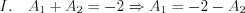
Let’s substitute the A1 coefficient into the II. equation
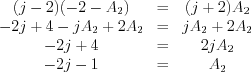 ,
,
as well as 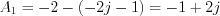 .
.
Consequently the general solution of the differential equation is:
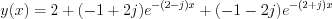
![$
y(x)=2+(-1+2j)e^{-2x}e^{jx}+(-1-2j)e^{-2x}e^{-jx}=2+e^{-2x}\left[(-1+2j)e^{jx}-(1+2j)e^{-jx}\right]](lib/equation/pictures/5b8922151d5b0fdbfb800456a411764d.png)
![$
y(x)=2+e^{-2x}\left[-e^{jx}+2je^{jx}-e^{-jx}-2je^{-jx}\right]](lib/equation/pictures/23555aec3926c019935294f7e6f09a7d.png)
![$
y(x)=2+e^{-2x}\left[-(e^{jx}+e^{-jx})+2j(e^{jx}-e^{-jx})\right]](lib/equation/pictures/c62ad5c894830d8d62d1d58ea910fe3d.png)
The following expression can be written by Euler’s formula:
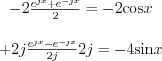
The solution is ![$y(x)=2+e^{-2x}\left[-2\text{cos}x-4\text{sin}x\right]](lib/equation/pictures/4ddf25c74b9f8965cdd4dd9f654bb0e4.png)
Let’s do some conversion at the final formula: it is known, that 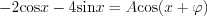 , where
, where 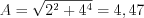 , and
, and 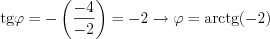
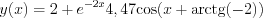
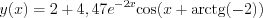
The original document is available at http://537999.nhjqzg.asia/tiki-index.php?page=S4.